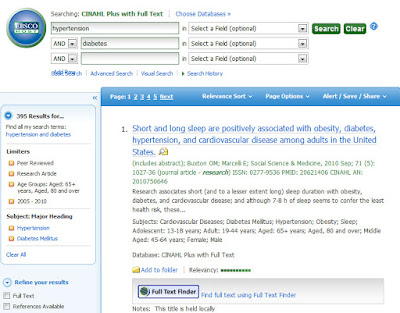
Keyword Example
Topic: research articles on treating hypertension in older people who also have diabetes.
- Open CINAHL by going to the Libraries’ website (http://www.apu.edu/library), clicking on “all databases” link, clicking on the letter “C”, and clicking on the link to “CINAHL with Full Text”.
- Do a keyword search for hypertension and diabetes (Note: to do a keyword search, leave the drop-down menus set to “Select a Field (optional)”.) Click SEARCH.
- Now click on “Show More” under “Refine your
results”, also in the blue column on the left.
- Click on the check box in front of “peer review” and “research articles"
- Then scroll down to “Age Group”, select Aged: 65+ years and Aged, 80 and over. Then click SEARCH.
- Click on the limiter, “Subject: Major Headings”
on the left in the blue column (you may have to scroll down.
- Click on the check box in front of Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus. Then click UPDATE.
- Limit dates as needed.
To view this search, click on the image below:
Why use a keyword search?
Keyword searches are useful if you are unsure of the exact name of the author(s), exact title of the information source or exact subject heading (descriptor) OR you are trying to find resources on a topic. Keywords are generally nouns in your research question or topic.
A keyword search retrieves records containing the term(s) you entered. The terms can appear in any of a number of fields (eg author, title, subject heading, contents or abstract, full text etc) of the record. You can limit your search so that the term appears in a specific field.
Read about some specific search strategies to help you locate resources that fit your topic.
Search Strategies & Tips
Some tips when conducting a keyword search (these tips may not apply to all databases, so be sure to check the HELP section of a specific database to find out more info):
- Truncation is represented by an asterisk (*). To use truncation, enter the root of a search term and replace the ending with an *. The search finds all forms of that word. For example: nurs* will search for nurse, nursing, nurses etc.
- The wildcard is represented by a question mark (?). To use the wildcard, enter your search terms and replace each unknown character with a ?. The search finds all citations of that word with the ? replaced by a letter. For example: wom?n; organi?ation
- If you want to replace more than 1 character use the hash symbol (#). For example: behavio#r; colo#r
- When a phrase is enclosed by double quotations marks. The search finds the the exact phrase. For example: "nursing theory"
- Use boolean operators such as and or or to specify multiple words in any field. Use not or and not to exclude words. We generally put AND between keywords and OR between synonyms. For example: hypertension or "high blood pressure" and diabetes or "high blood sugar"
- Use parenthesis or separate fields to group your synonyms. For example: (hypertension or "high blood pressure") and (diabetes or "high blood sugar")
Example:
Using the examples above our research topic is treating hypertension in older people who also have diabetes. (Keywords are highlighted in red.)
Synonyms:
- hypertension: high blood pressure
- diabetes: high blood sugar
- older people: elderly, 65+
Our search statement is: (hypertension or "high blood pressure") and (diabet* or "high blood sugar") and (elderly or "older people" or 65+)
- Introduction to Boolean Logic TutorialNeed more information about how boolean logic works as well as picture demonstrations.