What is Evidence Based Practice?
-
Evidenice Based Practice TutorialThis self-paced, interactive tutorial will take you through the complete EBP process, emphasizing the elements of a well-built clinical question and the key issues that help determine the validity of evidence. This program was developed by the Medical Center Library at Duke University and the Health Sciences Library at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
-
Appraisal ToolsAppraisal Tools in Word format (printable) from John Hopkins. Complete the form and click on submit.
-
Appraisal Tools ExampleThis chapter provides several examples of how teams can complete the JHEBP tools, and it gives helpful hints and guidelines to aid completion. The tools provided in this chapter reflect a brief overview of the project “EBP on Fall Prevention,” by H. Farley, E. Middleton, J. Kreif, L. Nell, E. Lins, and L. Klein as an exemplar. All tools shown are copyright protected by Johns Hopkins Health System/Johns Hopkins School of Nursing.

Head of Collections & Technical Services
Hugh & Hazel Darling Library #210
701 E. Foothill Blvd., PO Box 7000
Azusa, CA 91702
Books on EBP
-
Fast Facts for Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing by
Call Number: RT81.5 .G63 2020 EbookISBN: 9780826166234Publication Date: 2019-06-01 -
How to Read a Paper by
Call Number: R118.6 .G74 2019 EbookISBN: 9781119484738Publication Date: 2019-04-05 -
Models and Frameworks for Implementing Evidence-Based Practice by
Call Number: ebookISBN: 9781405175944Publication Date: 2010-05-10 -
Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing and Healthcare by
Call Number: RT42 .E954 2019ISBN: 9781496384539Publication Date: 2018-11-24
Contact Us and Research Help
Hours:
Research Help:
Contact Us:
- 24/7 Research Help
- Email us
- Schedule a Research Consultation
- Call Us: (626) 815-3847
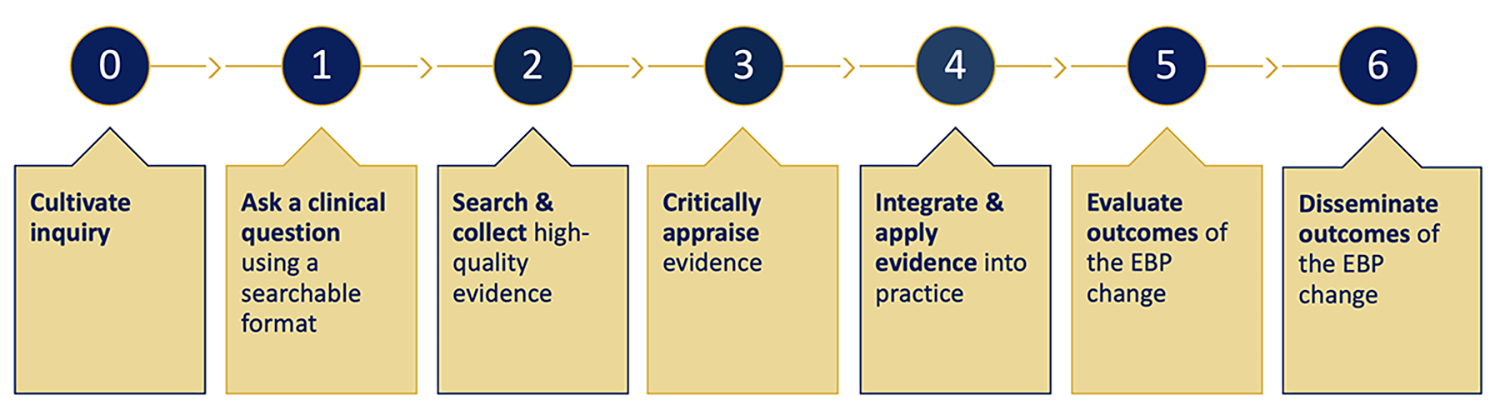
7 Steps Explained
The 7 Steps of Evidence-Based Practice:
A systematic approach to improving healthcare outcomes
-
What it means: Foster an environment where questioning current practices and seeking better ways to provide care is encouraged and supported. It's about asking, "Why do we do it this way?"
-
What it means: Formulate clear, answerable questions that guide your search for evidence.
-
PICOT stands for:
-
Patient/Population
-
Intervention/Interest
-
Comparison Intervention/Group
-
Outcome
-
Time (optional)
-
-
What it means: Systematically look for relevant research and evidence from reliable sources (e.g., databases like PubMed, CINAHL, Medline, Cochrane Library). Using a well-formulated PICOT question helps narrow the search.
-
What it means: Evaluate the quality, validity, reliability, and applicability of the gathered evidence to your clinical question. This involves assessing the research methods and findings.
-
What it means: Combine the best available research evidence with your own clinical experience and the individual patient's unique preferences, values, and circumstances to make a clinical decision.
-
What it means: After implementing a change based on EBP, measure and monitor its effects on patient outcomes, cost-effectiveness, and other relevant indicators. Is the change making a difference?
-
What it means: Share the findings and outcomes of your EBP initiative with others through presentations, publications, or internal reports. This helps to build the body of evidence and promotes further EBP implementation.
Melnyk, B. M., Fineout-Overholt, E., Stillwell, S. B., & Williamson, K. M. (2010). Evidence-based practice: step by step: The seven steps of evidence-based practice. AJN, American Journal of Nursing, 110(1), 51–53. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.NAJ.0000366056.06605.d2
Johns Hopkins Evidence-Based Practice for Nurses and Healthcare Professionals, 5th Edition 2025
Coming soon!
Johns Hopkins Evidence-Based Practice for Nurses and Healthcare Professionals, 4th Edition 2022
-
Johns Hopkins Evidence-Based Practice for Nurses and Healthcare Professionals, Fourth Edition by
Call Number: EbookISBN: 9781948057899Publication Date: 2021-07-15
- Front Cover
- Introduction
- Part I: Evidence-Based Practice Background
- Part II: The Johns Hopkins Evidence-Based Practice Model and Guidelines
- Part III: Practice Question, Evidence, Translation (PET)
- Part IV: Exemplars
- Part V: Using the JHEBP Tools
- Part VI: Appendices
- Appendix A: PET Process Guide (Downloadable in PDF)
- Appendix B: Question Development Tool (Downloadable in PDF)
- Appendix C: Stakeholder Analysis and Communication Tool (Downloadable in PDF)
- Appendix D: Hierarchy of Evidence Guide (Downloadable in PDF)
- Appendix E: Research Evidence Appraisal Tool (Downloadable in PDF)
- Appendix F: Nonresearch Evidence Appraisal Tool (Downloadable in PDF)
- Appendix G: Individual Evidence Summary Tool (Downloadable in PDF)
- Appendix H: Synthesis and Recommendations Tool (Downloadable in PDF)
- Appendix I: Translation and Action Planning Tool (Downloadable in PDF)
- Appendix J: Publication Guide (Downloadable in PDF)
- Appendices Downloadable in Word (complete form to download the documents in Word Format)
- Index
Articles on EBP in Nursing
-
The Impact of Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing and the Next Big IdeasThe impact of evidence-based practice (EBP) has echoed across nursing practice, education, and science. The call for evidence-based quality improvement and healthcare transformation underscores the need for redesigning care that is effective, safe, and efficient. In line with multiple direction-setting recommendations from national experts, nurses have responded to launch initiatives that maximize the valuable contributions that nurses have made, can make, and will make, to fully deliver on the promise of EBP. Such initiatives include practice adoption; education and curricular realignment; model and theory development; scientific engagement in the new fields of research; and development of a national research network to study improvement. This article briefly describes the EBP movement and considers some of the impact of EBP on nursing practice, models and frameworks, education, and research. The article concludes with discussion of the next big ideas in EBP, based on two federal initiatives, and considers opportunities and challenges as EBP continues to support other exciting new thinking in healthcare.
-
The Value of Library and Information Services in Nursing and Patient CareLibraries are a primary resource for evidence-based practice. This study, using a critical incident survey administered to 6,788 nurses at 118 hospitals, sought to explore the influence of nurses’ use of library resources on both nursing and patient outcomes. In this article, the authors describe the background events motivating this study, the survey methods used, and the study results. They also discuss their findings, noting that use of library resources showed consistently positive relationships with changing advice given to patients, handling patient care differently, avoiding adverse events, and saving time. The authors discuss the study limitations and conclude that the availability and use of library and information resources and services had a positive impact on nursing and patient outcomes, and that nurse managers play an important role both by encouraging nurses to use evidence-based library resources and services and by supporting the availability of these resources in healthcare settings.
"Evidence-based nursing (EBN) means using the best available evidence from research, along with patient preferences and clinical experience, when making nursing decisions.1 Nurses are increasingly concerned about ensuring that care is research based, and EBN offers a strategy to help nurses achieve this goal by using 5 steps:
Step 1: reflecting on practice and identifying areas of uncertainty
Step 2: translating these areas of uncertainty into focused, searchable questions2
Step 3: searching the literature for studies that use appropriate designs to help answer the question3–6
Step 4: critically appraising the research
Step 5: changing practice if the research suggests this is necessary." (Cullum, 2000)
- Asking Answerable Questions
- Reviewing the literature
- Searching for the best evidence. Part 1: where to look
- Searching for the best evidence. Part 2: searching CINAHL and Medline